Our neighbor planet Mars spins rapidly on its axis, and scientists aren’t sure what causes it.
The US space agency NASA announced on August 7 that experts were analyzing the data Intelligence module To monitor the speed of rotation of the planet.
They found that The length of a day on the Red Planet has been shortened by a fraction of a millisecond The whole planet rotates faster every year.
The team doesn’t really know what’s causing this acceleration, but they have a theory.
They suggest that it may be due to Overall, Mars changes slightlyFor example the mass of the planet or what happens on its surface.
Researchers believe this may be the cause Accumulation of ice on the polar caps or where the terrain rises after being buried by ice, is also called Post-glacial regeneration.
Until now, these changes in circulation could not be detected because There is no measurement as precise as the one recorded by the InSight moduleIt ceased operations this year after completing its extended tenure.
“It’s fantastic to be able to get this latest measurement with such precision,” said Bruce Bannert, InSight’s lead investigator.
“I’ve been involved in efforts to get a geophysical station like Inside to Mars for a long time, and results like this make those decades of work worthwhile.”
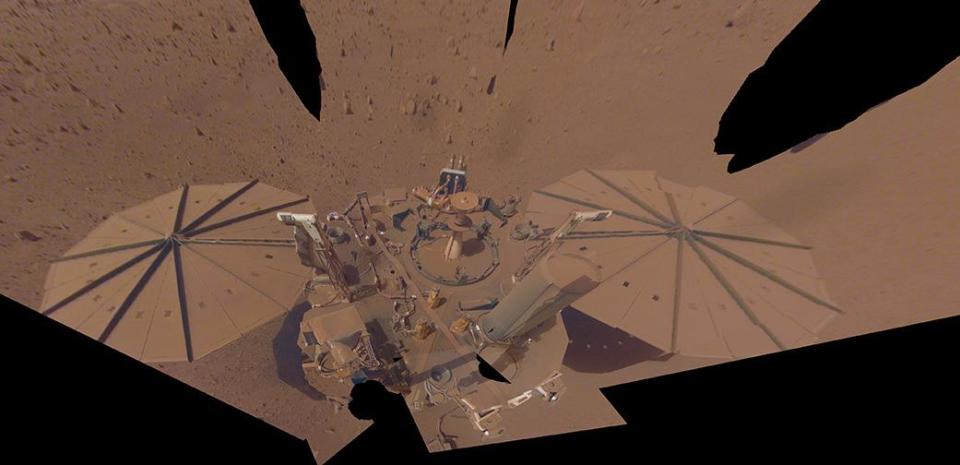
How are measurements made?
The InSight module was launched in May 2018 to help scientists understand more about the nature of the nearby planet.
On board he loaded Three main tools Action taken by: A SeismometerA Thermal analysis and a tool Radio wave measurement. Together they were called Rotational and Internal Structural Testing, or RISE, for its acronym in English.
The seismometer’s job is to patiently wait on the surface to detect pulses called seismic waves from Martian earthquakes and meteorite impacts.
A thermal probe measures the temperature below the surface. To do this, it is dug to a depth of about 5 m, which is the depth of the previous drilling or exploration.
For its part, the radio instrument tracked InSight’s exact location to determine how Mars moves around the Sun.
All this information was used by scientists who found the acceleration of the planet’s spin. Now they are trying to find out the possible reasons for this.
“Which We are looking for variations of a few tens of centimeters over the course of a Martian year,” said Sébastien Le Maistre, lead author of the paper and RISE Principal Investigator at the Royal Observatory of Belgium.
“It takes a lot of time and a lot of data Accumulated before we see these variations,” he added.
The study analyzed the first data 900 Tuesdays Recorded by Insight, enough time to look for such variations.


:quality(85)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/infobae/5W6S43NZDZED5EQX7RTQX4YJTA.jpg)