NASA / JBL-Caltech
An important part of the interplanetary communications infrastructure is being restored. NASA recently revealed How the Global Deep Space Network (DSN) will make more travel through the solar system and how it will enable communications in the future.
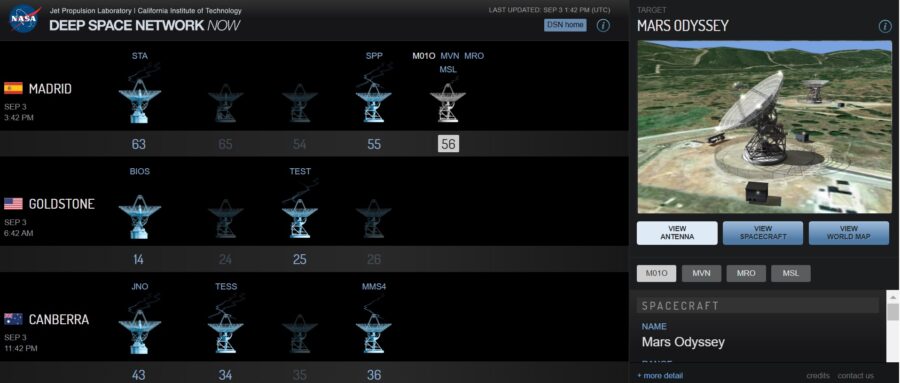
Founded in 1963 at the beginning of the Apollo era, DSN is made up of three platforms that provide global coverage: Madrid, outside of Spain; Goldstone, outside Barstow California; And the only base in the southern hemisphere in Canberra, Australia. If there is a spacecraft anywhere in the solar system beyond Earth, it will always be in view of at least one DSN site.
Each site is actually a collection of various radio antennas: a 70-meter main dish in Goldstone, three 34-meter dishes in Canberra and Goldstone, and four small dishes in Madrid.
POT
DSN typically supports 39 tasks in the solar system at a time, with an additional 30 tasks under development. When flying long-distance missions, data rates are very important: regular, for example Mars data rates On average, it runs at a speed of 500 to 32,000 bits per second, which is half the speed of a standard home modem. New Horizons I had to submit data in moderation 1,000 bits per second after the 2019 Arokot flybike.
“Capacity is a lot of pressure, our antenna upgrade program will help,” DSN Deputy Director Michael Levesque (JBL) said recently. Press release. “It involves the construction of two new antennas, increasing our number from 12 to 14.”
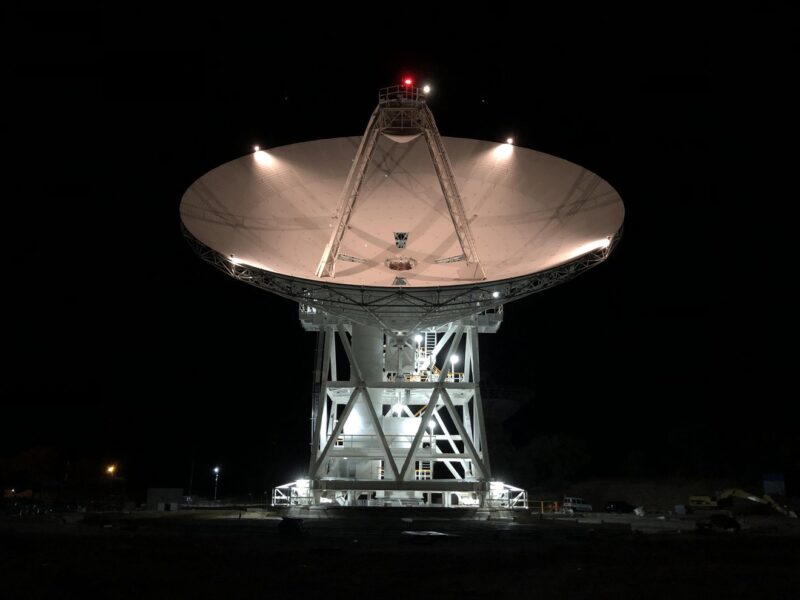
A new 34 meter plate (DSS-56It went into operation in Madrid in January 2021. Dish is an ‘all-in-one’ receiver and transmitter capable of transmitting communication frequencies on a large scale, rather than talking to trips assigned to specific frequencies as in the past. This capacity is specified for 34 new meters of food.
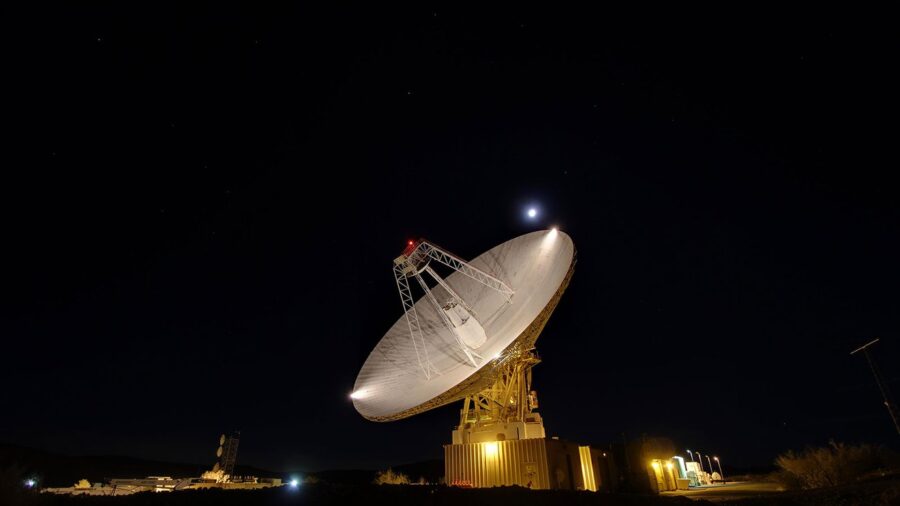
The team upgraded the larger 70-meter feed in Canberra, currently the only receiver that can talk to the Voyager 2 spacecraft, now more 127 astronomical units (au) Peacock, in the direction of the southern hemisphere galaxy Pao from the Sun.

NASA / JBL-Caltech
Updates are planned for the next major acquisitions of Madrid and Goldstone. These new systems can handle multiple signals on one antenna and separate them with a digital receiver, the simple ability to monitor multiple trips to Mars.
New approaches have also simplified the resources available to the DSN. For example, in the past, all sites tended to operate locally; Now, DSN operates under the mantra of “follow the sun”, where the daily change in each site controls the entire network, in a global hand.
“Each site works with other sites, not just during lead times, maintenance, and how the antennas work on a given day,” says Levesque. “We really have become a global operating network.”
Future assignments may include other types of communication. For example, NASA has tested optical laser line-of-sight communications. Lunar orbit lady Work and Plan for 2014 Many additional tasks To test infrared laser relays.
Often the first sign that the Mars lander is alive is the DSN that it can track. Live online.
POT
It’s great to see the great iconic web from deep space that guided the Apollo crew to the moon, food and spacecraft, rovers, and ultimately humans through the solar system.
Advertising




:quality(85)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/infobae/JVEG643FOJGGJFSNY3RS7DZM4I.jpg)
